

Permeated Whey and its functionalities
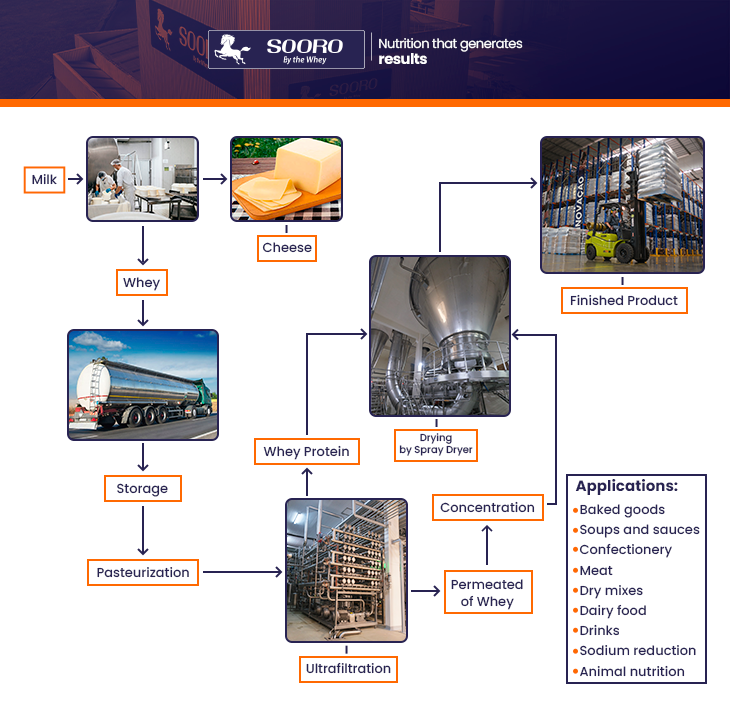
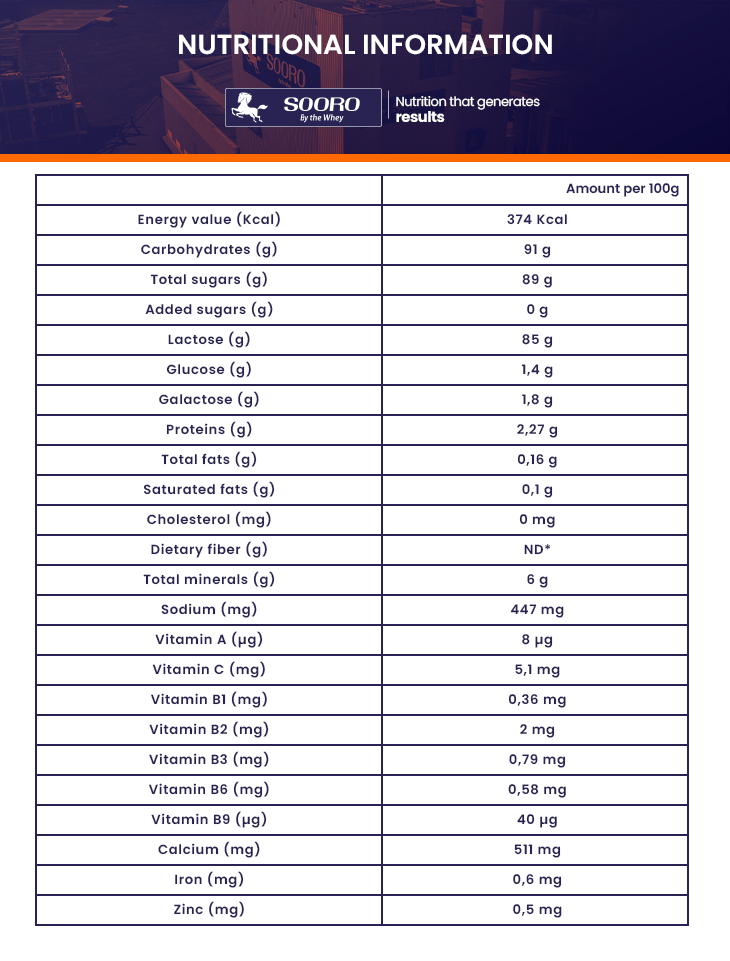
Permeated Whey is a byproduct of the dairy industry with a pleasant dairy flavor, obtained during the manufacturing process of Whey Protein. It is rich in milk-derived sugar and important minerals such as calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, sodium, and potassium, in addition to considerable amounts of B-complex vitamins and high-biological-value proteins.
During the manufacturing process, the liquid whey undergoes membrane treatments, usually ultrafiltration and diafiltration, to remove the soluble proteins in the whey, mostly β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin. This process results in a product with a high protein content (better known as WPC or Whey Protein) and Permeated Whey (a diluted fraction composed of lactose, mineral salts, electrolytes, nitrogen compounds, and water).
The Permeated Whey obtained by the membrane filtration process is concentrated by vacuum evaporators and then dried by a “spray dryer,” obtaining the Powdered Permeated Whey.
Its composition provides interesting nutritional and functional properties for different applications in the food industry, being suitable for various products for both human and animal consumption. It also has significant technological potential for developing new products.
Applications:
Permeated Whey can be used to enhance the flavor of foods, similarly to salt, and as an alternative to sodium, due to being an important source of dairy minerals, which is an excellent appeal for health-conscious industries, as it maintains the salty taste of products while reducing their sodium content. Furthermore, it can be used to fortify and enrich products with low levels of these nutrients.
In addition to reducing sodium in foods, the use of Permeated Whey can enhance the browning process and maintain the color of meat products, mask bitter flavors, and improve the structure of formation.
Permeated Whey, being rich in Milk Sugar, can replace other carbohydrates in formulations, providing a pure flavor to the product and a source of energy for consumers. Additionally, it can contribute to companies substituting sugar in their products’ formulations, allowing them to claim “no added sugar” and simplifying labels by reducing the listed ingredients (according to the new regulation – RDC429).
Permeated Whey also contributes to the golden color of baked products, improving their appearance and giving a caramelized flavor. It also has the ability to retain moisture, providing an additional benefit to baked products, helping them maintain their softness for an extended period and thus, extending their shelf life.
Permeated Whey is an excellent carrier of seasonings and dry flavors, helping to evenly disperse them in snacks or prepared dishes.
The use of Permeated Whey in milk-based broths and sauces perfectly harmonizes with the taste, texture, and creamy appearance. It can also be used in tomato-based soups and sauces to enhance their flavor and balance their acidity.
Permeated Whey can contribute to the nutritional composition of various beverages due to its carbohydrate and mineral content. Many beverages are fortified with vitamins and minerals, and the use of Permeated Whey allows product developers to add these minerals through a dairy source without relying on chemical sources.
Therefore, due to its physicochemical characteristics and the fact that it has competitive prices compared to milk and even whey, Permeated Whey can be used in a wide range of food formulations, such as meat products, dairy products, baking, confectionery, snacks, savory products, ice cream, food supplements, among others.
Peterson Vasconcellos Zequi, responsible for this content, has a degree in Biotechnology, a post-graduate degree in Project Management and New Product Development, and a Master’s degree in Food Science. He has been responsible for the Research and Development department of Sooro Renner since 2019, but has been a collaborator of the company since 2015.